Metals and Non Metals are some of the best required daily life components from day to day life and very important from scientific POV.
- About 118 elements are known today. There are more than 90 metals, 22 non-metals and a few metalloids.
- Sodium (Na), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), aluminium (Al), calcium (Ca), Iron (Fe), Barium(Ba) are some metals.
- Oxygen(O), hydrogen(H), nitrogen (N), Sulphur(S), phosphorus(P), fluorine(F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine(1) are some non-metals.
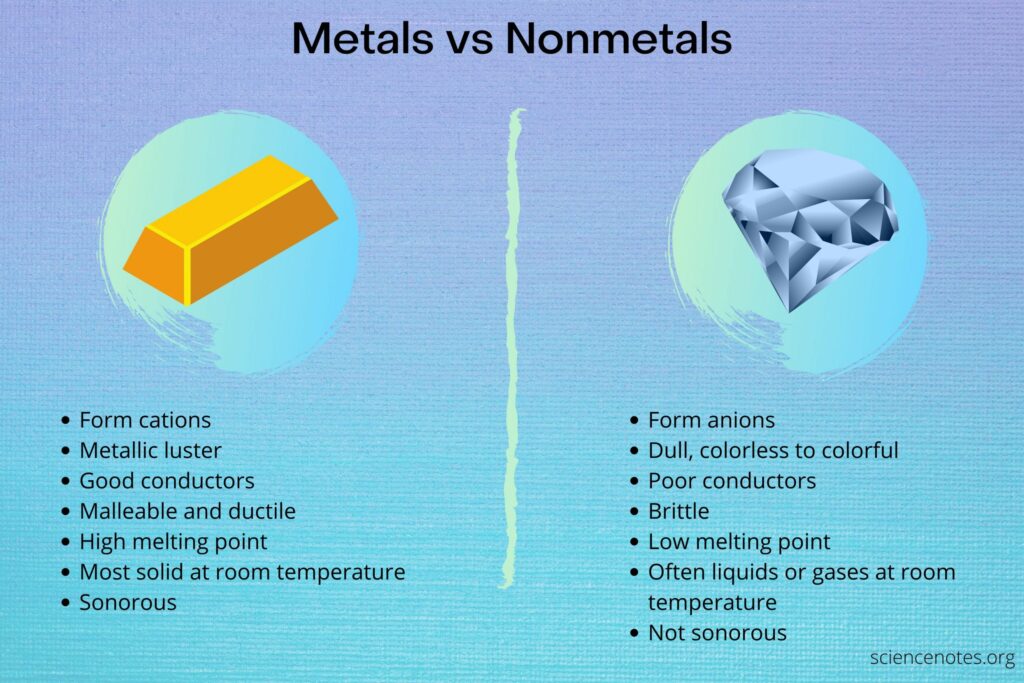
Physical properties of metals:
- Solid at room temperature except mercury.
- Ductile (drawn into wires)
- Malleable (beaten into thin sheets)
- Sonorous (produce sound)
- Lustrous (natural shine)
- Have high melting point. Caesium and gallium have very low melting point.
- Generally good conductor of heat and electricity, except lead and mercury which are comparatively poor conductors. Silver and copper are best conductors.
- Have high density. Sodium and potassium can be cut with knife, they have low density.
Below are some physical and chemical properties of metals and non metals.
Physical properties of non-metals:
- Occur as solid or gas. Bromine is liquid.
- Generally bad conductors of heat and electricity. Graphite a natural form of carbon is a good conductor.
- Non-sonorous.
- Non-lustrous, only iodine has luster.
- Metals form basic oxides like Magnesium oxide (MgO), while non-metals form acidic oxides (as in acid rain).
Get Offline education at OSF Education.
Chemical properties of metals:
- Reaction with air: Metals can burn in air, react or don’t react with air.
Metal+ oxygen→Metal Oxide
- Some metals like Na and K are kept immersed in kerosene oil as they react vigorously with air and catch fire.
- Some metals like Mg, Al, Zn, Pb react slowly with air and form a protective layer.
- Mg can also burn in air with a white dazzling light to form its oxide
- Fe and Cu don’t burn in air but combine with oxygen to form oxide.
When heated iron filings burn when sprinkled over flame.
- Metals like silver, platinum and gold don’t burn or react with air.
2Na+O2 → Na2O
2Mg+O2→ 2MgO
2Cu+O2→2CuO
4Al +3O2→2Al2O3
Amphoteric Oxides : metal oxides which react with both acids as well as bases to form salt and water
Read Other Articles here.
e.g. Al2O3 , ZnO
Al2O3+HCl →AlCl3+ H2O
Al2O3 +NaOH→NaAlO2 +H2O
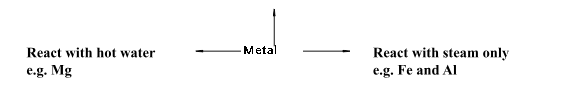
- Reaction with water :
React with cold water e.g. Na, K, Ca
Na+ H2O → NaOH +H2
K + H2O → KOH +H2
Ca +H2O →Ca(OH)2 +H2
Mg+H2O → Mg(OH)2 + H2
In case of Ca and Mg, the metal starts floating due to bubbles of hydrogen gas sticking to its surface
Al +H2O → Al2O3 + H2
Fe +H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
- Reaction with dilute acids :
Metal + dilute acid→ Salt + Hydrogen gas
Metal react with dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute sulphuric acid to form salt and hydrogen gas.
Fe + 2HCl→ FeCl2 + H2
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + H2
Copper, mercury and silver don’t react with dilute acids.
Hydrogen gas produced is oxidized to water when metals react with nitric acid. But Mg and Mn, react with very dilute nitric acid to evolve hydrogen gas.
Mg + 2HNO3 → Mg(NO3)2 + H2
- Reaction of metals with other metal salts:
Salt Salt
Metal A + Solution of B → Solution of A + Metal B
- All metals are not equally reactive. Reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution. This forms the basis of reactivity series of metals.
- Reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in order of their decreasing activities.
K
Na Most Reactive
Ca
Mg
Al
Zn Decreasing Reactivity
Fe
Pb
H
Cu
Hg
Ag
Au Least Reactive

Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Reaction between Metals and Non-Metals:
- Reactivity of elements can be understood as a tendency to attain a completely filled valence shell.
- Atom of metals can lose electrons from valence shells to form cations (+ve ions).
- Atom of non-metals gain electrons in valence shell to form anions (-ve ions).
- Oppositely charged ions attract each other and are held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction forming ionic compounds.
Formation of MgCl2
Mg → Mg2+ + 2e–
2, 8, 2 2,8 (Magnesium ion)
Cl2 + 2e–→ 2Cl–
2, 8, 7 2,8,8 (Chloride ion)
Properties of lonic Compounds:
- Are solid and mostly brittle.
- Have high melting and boiling points. More energy is required to break the strong inter-ionic attraction.
- Generally soluble in water and insoluble in kerosene, petrol.
- Conduct electricity in solution and in molten state. In both cases, free ions are formed and conduct electricity.
Occurrence of Metals
Minerals: elements of compounds occurring naturally are minerals
ORES: mineral from which metal can be profitably extracted is an ore. For example, sulphide ore, oxide ore, carbonate ore.
- Metals at the bottom of activity series like gold, platinum, silver, copper generally occur in free state. But copper and silver also occur in sulphide and oxide ores.
- Metals of medium reactivity (Zn, Fe, Pb etc.) occur mainly as oxides, sulphides or carbonates.
- Metals of high reactivity (K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al) are very reactive and thus found in combined state.
GANGUE: ores are naturally found mixed impurities like soil, sand, etc. called gangue. The gangue is removed from the ore. ore.
METALLURGY: stepwise process of obtaining metal from its
- Enrichment of ore
- Obtaining metal from enriched ore.
- Refining of impure metal to obtain pure metal.
Extracting Metals Low in the Activity Series:
By heating the ores in air at high temperature.
Mercury from cinnabar
2HgS + 3O2 (Heat )→ 2HgO + 2SO2
2HgO (Heat)→ 2Hg + O2
Copper from copper sulphate
Cu2S + 3O2(Heat)→ 2Cu2O + 2SO2
2Cu2O +Cu2S(Heat)→6Cu +SO2
Extracting Metals in the Middle of Activity Series:
- Metals are easier to obtain from oxide ores, thus, sulphide and carbonate ores are converted into oxides.
- Metal ore heated strongly in excess of air (Roasting)
2ZnS + 3O2(Heat)→ 2znO+2SO2
Metal ore heated strongly in limited or no supply of air (Calcination)
ZnCO3( Heat)→ ZnO + CO2
Reduction of Metal Oxide:
- USING COKE:
- Coke as a reducing agent.
- ZnO + C( Heat)→ Zn + CO
- USING DISPLACEMENT REACTION: highly reactive metal like Na, Ca and Al are used to displace metals of lower reactivity from their compounds.
MnO2+ 4Al(Heat) → 3Mn+2Al2O3 + heat
Fe2O3+ 2Al (Heat )→ 2Fe+Al2O3+ heat
- In the above reaction molten iron is formed and is used to join railway tracks,
This is called thermit reaction.
Extracting Metals at the Top of Activity Series:
These metals
- have more affinity for oxygen than carbon.
- are obtained by electrolytic reduction. Sodium is obtained by electrolysis of its molten chloride
NaCl(Heat)→Na+ + Cl–
As electricity is passed through the solution metal gets deposited at cathode and non-metal at anode.
- At cathode: REDUCTION by gain of electron.
Na++e– (Heat)→ Na
- At anode: OXIDATION by loss of electron.
2Cl– (Heat)→ Cl2 + 2e–
Refining of Metals:
- Impurities present in the obtained metal can be removed by electrolytic refining.
- Copper is obtained using this method. Following are present inside the electrolytic tank.
- Anode – slab of impure copper
- Cathode-slab of pure copper
- Solution – aqueous solution of copper sulphate with some dilute sulphuric acid
- From anode copper ions are released in the solution and equivalent amount of copper from solution is deposited at cathode.
- Impurities containing silver and gold gets deposited at the bottom of anode as anode mud.
Corrosion:
- Metals are attacked by substances in surroundings like moisture and acids.
- Silver – it reacts with sulphur in air to form silver sulphide and articles become black.
- Copper – reacts with moist carbon dioxide in air and gains a green coat of copper carbonate.
- Iron-acquires a coating of a brown flaky substance called rust Both air and moisture are necessary for rusting of iron.
Prevention of corrosion:
- Rusting of iron is prevented by painting, oiling, greasing, galvanizing, chrome plating, anodizing and making alloys.
- In galvanization, iron or steel is coated with a layer of zinc because zinc is preferably oxidized than iron.
Alloys:
- These are mixture of metals with metals or non-metals
- Adding small amount of carbon makes iron hard and strong.
- Stainless steel is obtained by mixing iron with nickel and chromium. It is hard and doesn’t rust.
- Mercury is added to other metals to make amalgam.
Brass: alloy of copper and zinc.
Bronze: alloy of copper and tin.
- In brass and bronze, melting point and electrical conductivity is lower than that of pure metal.
Solder:
- alloy of lead and tin has low melting point and is used for welding electrical wires.

