- In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the objects.
- We will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical phenomena in nature
- i.e. Rainbow formation, twinkling of star, blue and red color of sky etc.
Human Eye: A Sensitive sense organ
It acts like a camera, enable us to capture the colorful picture of the surroundings. It forms an inverted, real image on light sensitive.
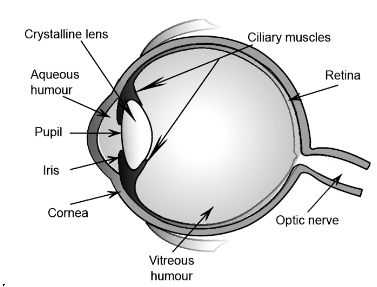
The Various parts of eye and their functions
- Cornea: It is a thin membrane through which light enters. It forms the transparent bulge on the front of eyeball. Most of the refraction occurs at the outer surface of the cornea.
- Eyeball: it is approximately spherical in shape, with a diameter of about 2.3em.
- Iris: It is a dark muscular diaphragm that controls the size of pupil. It is behind the cornea.”
- Pupil: It regulates and control the amount of light entering the eye. It is the black opening between aqueous humour & lens.
- Crystalline eye lens: Provide the focused real & inverted image of the object on the retina. It is composed of a fibrous, jelly like material. This is convex lens that converges light at retina.
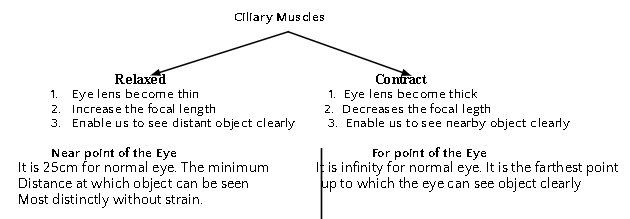
- Ciliary muscles: It helps to change the curvature of eye lens and hence changes its focal length so that we can see the object clearly placed at different position.
- Retina: Thin membrane with large no. of sensitive cells.
Join Offline Classes at OSF Education.
Read more class 10 notes at here.
- When image formed at retina, light sensitive cells gets activated and generate electrical signal. These signals are sent to brain via optic nerve. Brain analyses these signals after which we perceive object as they are
How pupil works?
Example: You would have observed that when you come out of the cinema hall after watching movie in the bright sun light, your eyes get closed. And when you entered the hall from the bright light, you won’t be able to see and after some time you would be able to see.
Here the pupil of an eye provides a variable aperture, whose size is controlled by iris
a) When the light is bright: Iris contracts the pupil, so that less light enters the eye.
b) When the light is dim: Iris expand the pupil, so that more light enters the eye. Pupil open completely, when iris is relaxed.
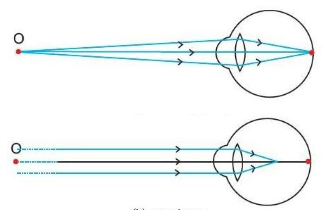
Persistence of Vision: It is the time for which the sensation of an object continue in the eye. It is about 1/16″ of a second.
Power of Accommodation:
The ability of eye lens to adjust it focal length is called accommodation with the help of ciliary muscles.
DEFECTS OF VISION AND THEIR CORRECTION
- CATARACT: The image cannot be seen distinctly because eye lens become milky and cloudy. This condition is known as cataract, it can cause complete or partial loss of vision. This can be corrected by surgical removal of extra growth (cataract surgery)
- Myopia: (Near Sightedness)
A person can see nearby object clearly but cannot see distant object distinctly.
Image formed in front of the retina.
The Reason of defect
- Excessive curvature of eyes lens (thick, decrease focal length)
- Elongation of the eye ball.
CORRECTION
Corrected by using a Concave lens of appropriate power.
- Hypermetropia (Far – Sightedness) –
A person cannot see nearby object clearly but can see distant object distinctly.
Image formed at a point behind the retina
The Reason of defect
- Increase in focal length of the eye lens (Thin eye lens)
- Eye ball has become too small.
CORRECTION
Corrected by using a Convex Lens of appropriate power.
- Presbyopia
As we become old, the power of accommodation of the eye usually decreases, the near point gradually recedes away.
This defect is called Presbyopia. Person may suffer from both myopia and hypermetropia.
Reason of defect- Gradual weakening of ciliary muscles and decreasing the flexibility of the eye lens.
Correction- Using of Bifocal lens with appropriate power.
Bifocal lenses consist of both concave and convex lens, upper position consist of concave lens and lower portion consist of convex lens.
Refraction of light through a Prism
Prism- It has two triangular bases and three rectangular lateral surfaces. These surfaces are inclines to each other. The angle between its two lateral faces is called Angle of Prism
Angle of Deviation (D) 🡪 The angle between the incident ray and emergent ray. Dispersion of white light by a Glass Prism
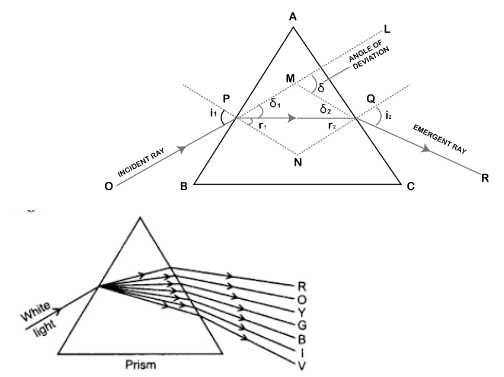
Inclined refracting surfaces of glass prism show exciting phenomenon.
Splitting of White light into band of colors
- The band of the colored components of light beam as called Spectrum i.e. VIBGYOR
- The splitting of light into its component colors is called Dispersion.
- The different component color of light bends at different angle with respect to incident angle the red light bends the least while the violet bends most.
ISSAC NEWTON
- He was the first, who obtained spectrum of sunlight by using glass prism.
- He tried to split the spectrum of white light more by using another similar prism, but he could not get any more colors.
- He repeated the experiment using second prism in on inverted position with respect to the first prism.
- Allowed all the colors of spectrum to pass through second prism. He found white light emerges on the other side of second prism.
- He concluded that sun is made up of seven visible color ‘VIBGYOR’
RAINBOW
- It is the spectrum of sunlight in nature It is formed due to the dispersion of sunlight by the tiny water droplet, present in atmosphere.
Water droplet act like prism.
It refracts and disperse the incident sunlight, then reflect it internally (internal reflection) and finally refract it again, when it emerges out of the water droplet.
A rainbow is always form in a direction opposite to that of sun.
Due dispersion and internal reflection of light different color reaches to observer’s eye.
Red colour appear on top & violet at the bottom of rainbow
Atmospheric Refraction –
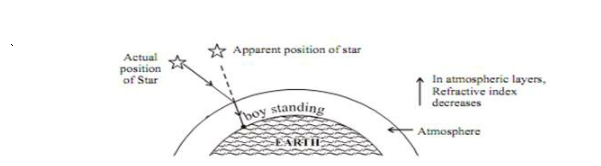
- Apparent Star Position- It is due to atmospheric refraction of starlight.
The temperature and density of different layer of atmosphere keeps varying. Hence, we have different medium.
Distant star act as point source of light. When the starlight enters the earth’s atmosphere it undergoes refraction continuously, due to changing refractive index i.e. from Rarer to denser. It bends towards the normal.
Due to this the apparent position of the star is different from actual position. The star appears higher than its actual position
- Twinkling of Star-It is also due to atmospheric refraction
Distant star act like a point source of light. As the beam of starlight keeps deviating from its path, the apparent position of star keeps on changing because physical condition of earth’s atmosphere is not stationary
Hence the amount of light enters our eyes fluctuate some time bright and sometime faint.
This is the “Twinkling effect of star”
Q. Why Planet do not twinkle?
Ans. Planets are closer to earth and are seen as extended source of light i.e. the collection of large no: of point sized sources of light. Therefore, the total amount of light entering our eyes from all individual point source will nullify the twinkling effect
Q. Why Planet do not twinkle?
Ans. Planets are closer to earth and are seen as extended source c light i.e. the collection of large no: of point sized sources of light. Therefore, the total amount of light entering our eyes from all individual point source will nullify the twinkling effect.
(3) Advance Sunrise and delayed sunset
This is also due to atmospheric refraction.
Because of this sun is visible about 2 minutes earlier than actual sunrise and about 2 minutes after the actual sun set.
Apparent flattering of the sun’s disc at sun set and sun rise is due to atmospheric refraction.
Scattering of Light
Tyndall Effect– When a beam of light strikes the minute particle of earth’s atmosphere suspended particles of dust and molecule of air the path of beam become visible. The phenomenon of scattering of light by the colloidal particle gives rise to Tyndall Effect.
It can be observed when sunlight passes through a canopy of a dense forest. The colour of the scattered light depends on the size of the scattering particles.

- Why cloud Appear white– The size of water droplet (scattering particle) is very large, hence scattered all wavelength of light almost equally.
- Why color of sky is blue– The molecules of air and other fine particles in the atmosphere have size smaller than the wavelength of visible light. Since the blue has shorter wavelength than red, hence it will scatter the most
According to Rayleigh scattering,
Scattering of light proportional 1/4λ , Where λ is wavelength
- Scattering of light decreases with increasing of wavelength.
Q. If there is no earth’s atmosphere? What will happen to be scattering phenomenon?
Ans. There will be no scattering and sky will appear dark.
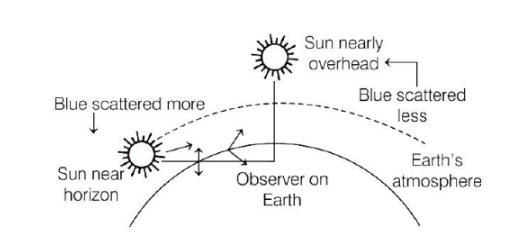
(3) Color of the Sun of Sunrise and Sunset
While sunset and sunrise, the color of the sun and its surrounding appear red.
During sunset and sunrise, the sun is near horizon, and therefore the sunlight must travel larger distance in atmosphere. Due to this most of the blue light (shorter wavelength) are scattered away by the particles. The light of longer wavelength (red color) will reach our eye. Therefore, sun appear red in color.
(4) Why the danger signal or sign are made of red color.
Red color scattered the least when strikes the small particle of fog and smoke because in has the maximum wavelength (visible spectrum). Hence at large distance also, we can see the red color clearly.
(5) At noon sun appear white-
At noon the, sun is overhead, and sunlight would travel shorter distance relatively through the atmosphere. Hence, at noon, the Sun appear while as only little of the blue and violet colors are scattered.