Chemical Reactions

Whenever a chemical change occurs, we can say that a chemical reaction has taken place
e.g. – Food gets digested in our body
– Rusting of iron.
Chemical Equation:- A chemical reaction can be expressed symbolically by using a chemical equation
e.g. magnesium is burnt into the air to form magnesium oxide can be represented as
Mg+O2 → MgO
We can observe or recognize a chemical reaction by observing a change in state, or color, by the evolution of gas, or by the change in temperature.
- The physical state of the reactant and products are mentioned to makes chemical reaction more informative.
- e.g. we use (g) for gas, (l) for liquid, (s) for solid, and (aq) for aqueous.
- Balancing Equation :- We balance the chemical equation so that no. of atoms of each element involved in the reaction remain same at the reactant and product side.
e.g. Fe+ H2O → Fe2O3 + H2 can be written as
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4 + 4H2(g)
Read More about Balancing Equation
- Combination Reaction: The reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a new single substance
e.g. CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
Calcium Oxide Water Calcium hydroxide
( Quick Lime) (Slaked lime)
- Ca(OH), slaked lime is used for white washing walls. It reacts with CO₂ to form CaCO2 and gives a shiny finish to the walls.
Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO2(s) + H2O(l)
Calcium hydroxide Calcium Carbonate
Exothermic Reactions : – Reaction in which heat is released along with the formation of products.
e.g. CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
Respiration is also exothermic reaction.
De composition of vegetable matter into compost.
Decomposition Reactions : – The reaction in which a single substance decomposes to give two or more substances.
Decomposition reactions can be of three types
- Types of Decomposition Reactions
Thermal Decomposition : – When a decomposition reaction is carried out by heating
e.g. 2FeSO4(S) Fe2O3(g) + SO2 + SO3
Ferrous Sulphate Ferric Oxide
Green Color Reddish brown color
CaCo3(S) Cao(g) + CO2(g)
PB(NO3)2(s) PbO(S) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
Lead Nitrate Lead Oxide Nitrogen Oxygen
White colour Brown colour Dioxide
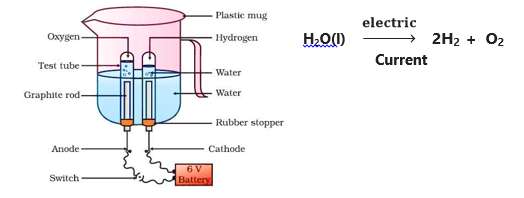
Electrolytic Decomposition : – When a decomposition reaction is carried out by electric current,
e.g. H2O(l)
Photolytic Decomposition : – When a decomposition reaction is carried out by light
e.g. 2AgCl(S) 2Ag(S) + Cl2(g)
White color grey color
Silver bromide behaves similarly
2AgBr 2Ag(S) + Br2 (g)
The above two reactions are used in black and white photography.
Endothermic Reactions : – The reactions which require energy in the form of heat, light or electricity are called Endothermic Reactions.
2Ba(OH)2 + NH4Cl → 2BaCl2 + NH4OH
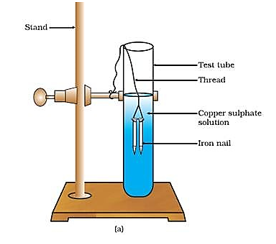
Displacement Reaction : – The chemical Reaction in which an element displaces another element from its solution. This
depends on reactivity series.
Fe(S) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4 + Cu(s)
Copper (aq)
Sulphate Iron Sulphate
The nail becomes brownish in color and the blue color of Copper Sulphate solution fade.
Other examples :-
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4 + Cu(S)
Copper Zinc
Sulphate Sulphate
Pb(S) + Cucl2(aq) → PbCl2 (aq) + Cu(S)
Copper Lead
Chloride Chloride
Zinc and lead are more reactive elements than copper. They displace copper from its compounds.
Double Displacement Reaction : – The reaction in which two different atoms or group of atoms are mutually exchanged
e.g. Na2 SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(S) + 2Nacl(aq)
Sodium Sulphate Barium Chloride Barium Sulphate Sodium Chloride
A white substance is formed due to above reaction. The insoluble substance is called precipitate.
Precipitate Reaction : – Any reaction that produces a precipitate is called a precipitation reaction.
e.g. Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI → PbI2(aq)¯ +2KNO3
Lead Nitrate Potassium Lead Ptassium
Iodide Iodide Nitrate
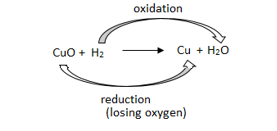
Oxidation : Oxidation is the gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen or loss of electron.
e.g. 2Cu + O2 2CuO
When Copper is heated a black color appears. If this CuO is reacted with hydrogen gas then again, Cu becomes brown as reverse reaction takes place CuO + H2 Cu +H2O
Reduction : Reduction is the loss of oxygen or gain of hydrogen.
Redox Reaction : The reaction in which one reactant gets oxidized while other gets reduced
e.g. ZnO + C Zn + CO
MnO2 + 4HCl MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
Corrosion :
- When a metal is exposed to moisture, air, acid, etc. for some time, a layer of hydrated oxide is formed which weakens the metal and hence metal is said to be corroded.
- Rusting of iron, black coating on silver and green coating on copper are examples of corrosion.
- Corrosion can be prevented by painting, oiling, galvanization (Zn metal- layer), electroplating.
Rancidity :
When fats and oils are oxidized, they become rancid and their smell and taste change.
Methods to prevent rancidity
- By adding antioxidants
- Keeping food in air tight containers
- Replacing air by nitrogen
- Refrigeration.
Read More at – MonoMath