- Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals like themselves
- Reproduction ensured continuity of life on earth.
- Reproduction- A bridge to hereditary transmission
- It involves continuation of characters from the parents to daughter cells by Copying of DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) molecules present in the chromosomes of the cell.
- Copying of DNAs is also not a foolproof exercise, even minute changes bring about Variation in the blueprint of the off springs.
- The useful variations are retained while the harmful one does not go beyond.
- Variations help the species to withstand drastic environmental changes, thus save the species from becoming extinct and promotes its survival for a longer time.
- This inbuilt tendency of variation is the “fuel” for Evolution
Join Offline classes at OSF Education.
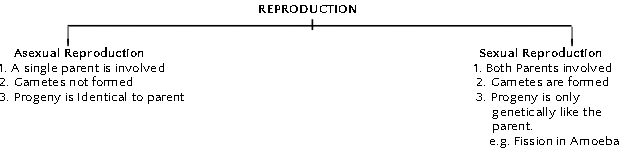
- Asexual Reproduction is extremely useful as a mean of rapid multiplication. It is common in lower plants and animals.
- Different form of Asexual Reproduction.
Read More Notes here
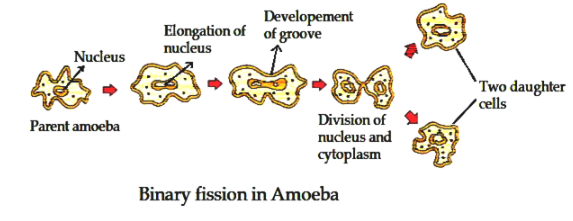
- FISSION: the parent cell divides/splits into two daughter cell-Binary Fission; splits into many cells-multiple Fission
- BUDDING: A new organism is produced as an outgrowth of the parent body part.
- Spore Formation: Spores are small, bulb like structure develops at the top of the erect hyphae of the fungus plant, released into the air and germinate, into new individuals after landing into food or soil. e.g. Rhizopus
- FRAGMENTATION: It broken pieces of an organism (tragments) grows into a complete organism
- REGENERATION: When the simple animals like Hydra. Planaria develop a new individual from their broken older part it is known as regeneration. It is carried out by specialized cells which grow large numbers of cells.
VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION:
- A mode of reproduction in which part like the stem, root, leaves develop into new plant under favorable conditions.
Benefits
1. Plants can bear flowers, fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
2. Growing Banana, orange, rose, jasmine that have lost the capacity to produce seeds.
3. Genetical similarity is maintained in the plants. e.g. Sugarcane, rose, grapes by layering or grafting.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
- When reproduction takes place as a result of fusion between two gametes, one from each parent, it is called sexual reproduction.
- This process of fusion between two gametes is called fertilization.
- The formation of gametes involves exchange of chromosomal (genetic) fragments between homologous chromosomes causing genetic recombination which leads to variation.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
- It occurs mostly in flowering plants. In fact, flowers are the reproductive organ of plants.
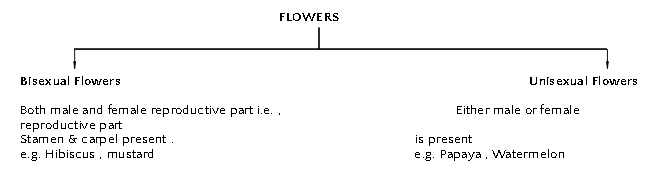
A typical flower consists of four main whorls namely calyx(sepals), Corolla(Petals), Androecium(stamens) and Gynoecium(Carpels).
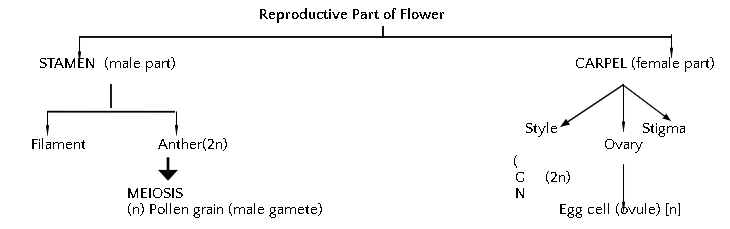
- Pollen grains of a flower transfer to stigma of the carpel of the same flower or to the carpel of another flower.
- This transfer of pollens is achieved by agent like wind, water or animals.
- After Pollination, the pollen grains reach to the egg cell in the form of a pollen tube.
Fertilization: The fusion between the pollen grain and female egg cell. It occurs inside the ovary. Zygote is produced in this process.
- Zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat and is converted into a seed.
- Ovary grows rapidly and ripens to forms a fruit, while the seed contains the future plant or embryo which develops into a seedling under suitable condition. This process is known as Germination.
REPRODUCTION IN HUMAN BEINGS
- Humans use a Sexual Mode of reproduction.
- It needs sexual maturation which includes creation of the germ cells i.e., egg (ova) in the female and sperm in the male partner & this period of sexual maturation is called Puberty.
- Human beings have a well-developed male and female reproductive system.
- The formation of male germ cell (sperms) takes place in the testes (male reproductive organ)
- Actually, a pair of testes are located inside scrotum situated outside the abdominal cavity. It is meant to keep relatively a low temperature needed to produce sperms by testes.
- Moreover, testes release a male sex hormone called testosterone whose function is to:
1. Regulate the production of sperm
- Brings about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty.
- The sperms along with the secretion of prostate gland and seminal vesicle, together constitute semen, which is released and made to enter the female genital tract during Copulation.
- The female germ cells or eggs are made in the ovaries, a pair of which is located in both side of abdomen.
- When a girl is born, the ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs.
- At the puberty, some of these Eggs start maturing. One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
- The Egg is carried from the ovary to the womb through a fullopian tube. These two fallopian tubes unite into an elastic bag like structure known as Uterus.
- The Uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix. Fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube of female genital tract.
- The fertilized egg also called zygote (2n) gets implanted in the lining of the Uterus and start dividing. Actually, uterus is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing embryo. If zygotes not formed, the inner wall of uterus breaks which causes bleeding through vagina. This process is MENSTRUATION. It occurs at a regular interval of 28 days.
- The Embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called PLACENTA. It provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo. Similarly, the wastes from developing embryo are removed to mother’s blood through placenta.
- The child is born as a result of rhythmic contractions of the muscles in the uterus. after Nine months (36 weeks) of development inside mother’s womb. It is also called Gestation Period.
- The sexual cycle in a woman continues up to the age of 45 to 50 years. After that the ovary do not release egg. This stage is called Menopause. It also marks the end of menstruation in the woman.
REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
- Reproductive Health means a total well-being in all aspects of reproductive, i.e… physical emotional, social and behavioral
- Contraception: It is the avoidance of pregnancy. It can be
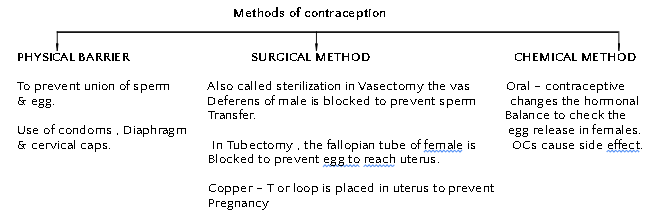
Healthy society needs a balanced sex ratio that can be achieved by educating the people to avoid malpractices like female feticide & pre-natal sex determination.