- All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc.
- All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living organisms alive and perform the job of body maintenance are called life processes.
EXAMPLES:
Autotrophic Nutrition an Important Life Process
- The organisms which carry out autotrophic nutrition are called autotrophs (green plants)
Autotrophs(Use) →Simple in organic material(Convert) → Complex high energy
Into molecules Carbohydrates
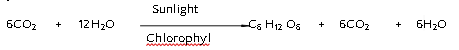
- Autotrophic nutrition is fulfilled by the process by which autotrophs take in CO, and H,O and convert these into carbohydrates in the presence of chlorophyll, sunlight is called PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Join Offline classes at – OSF Education
Read More at – MonoMath
Equation:
Raw Materials for Photosynthesis:
- Sunlight
- Chlorophyll Sunlight absorbed by chlorophyll
- CO2 enters through Stomata and Oxygen is released as by product through stomata on leaf.
- Water water + dissolved minerals like Nitrogen phosphorous etc. are taken up by the roots from the soil.
Site of Photosynthesis:
Chloroplast in the leaf. Chloroplast contain chlorophyll. (green pigment)
Main Events of Photosynthesis:
- Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
- Conversion of light energy into chemical energy + splitting (breaking) of water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Reduction of CO, to carbohydrates.
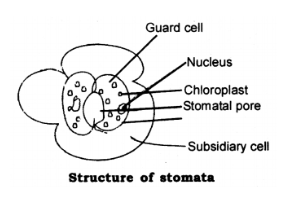
STOMATA: Tiny pores present on the surface of the leaves
FUNCTIONS:
- Exchange of gases O₂/CO₂
- Loses large amount of water [water vapors] during transpiration.
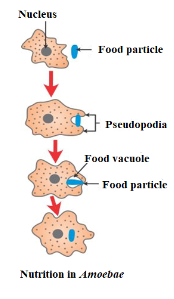

How do organisms obtain their food
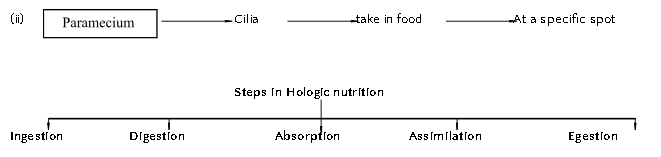
Unicellular / Single celled organism : Food is taken up through entire surface. Example : (i) Amoeba
(ii) Paramaecium
NUTRITION IN HUMAN BEINGS
The human digestive system comprises of alimentary canal and associated digestive

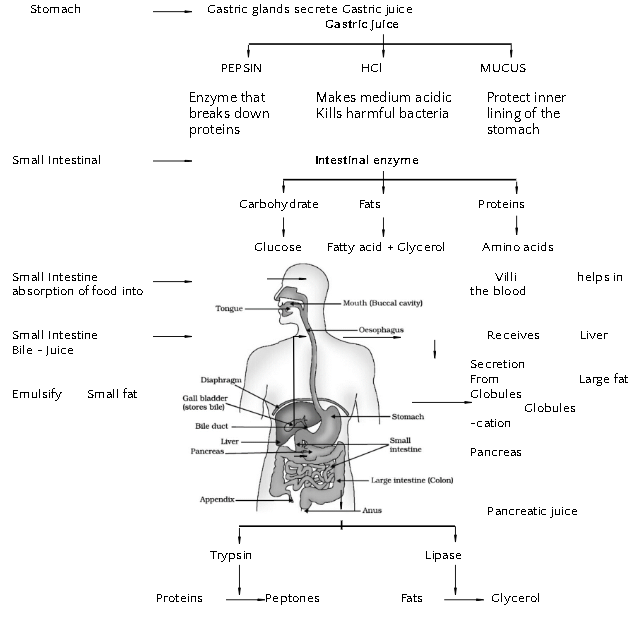
Emulsification: The process of breakdown of large fat globules by bile juice
Large intestine —–>Absorb excess of water.
—–>The rest of the material is removed from the body via the anus (Egestion).
Respiration
- Gaseous exchange : Intake of oxygen from the atmosphere and release of CO2 Breathing
- Breakdown of simple food in order to release energy inside the cell Cellular Respiration
Breakdown of Glucose by various pathways
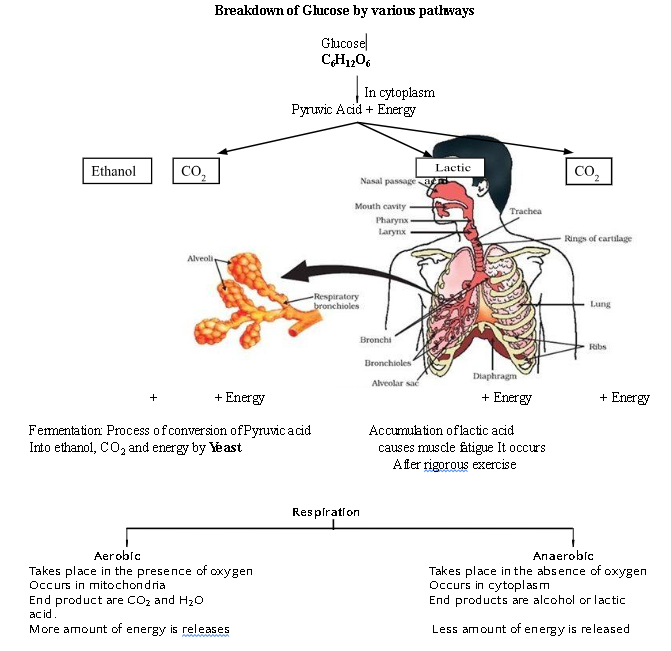
Human Respiratory System
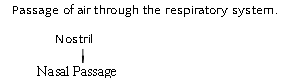
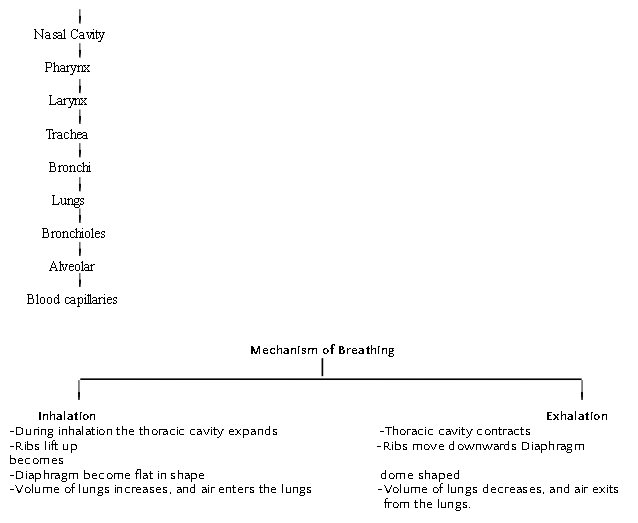
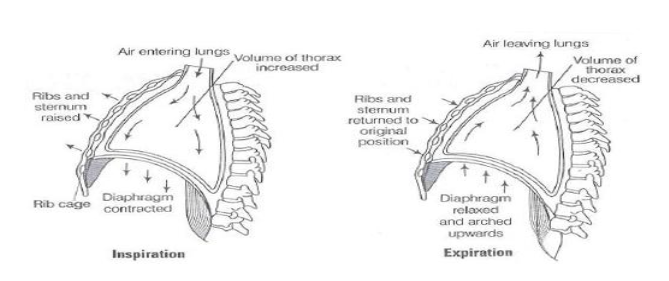
Exchange of Gases between alveolus, blood and tissues.
O2
- Air (rich in O2) ———–> Blood ———–> Binds with Haemoglobin
(in alveolus) [ through blood vessels] in RBC
O2 is released in tissues

Terrestrial Organism – use atmospheric oxygen for respiration
Aquatic Organisms – used dissolved oxygen for respiration.
Respiration in plants: Respiration in Plants is simpler than the respiration in animals. Gaseous exchange occurs through
- Stomata in leaves
- Lenticels in stems
- General surface of the roots.
Life Process
Transportation and Excretion
- Human beings like other multicellular organism need regular supply of food, oxygen etc., This function is performed by circulatory system or Transport system.
The circulatory system in human beings consists of: The circulatory system in human beings consists of
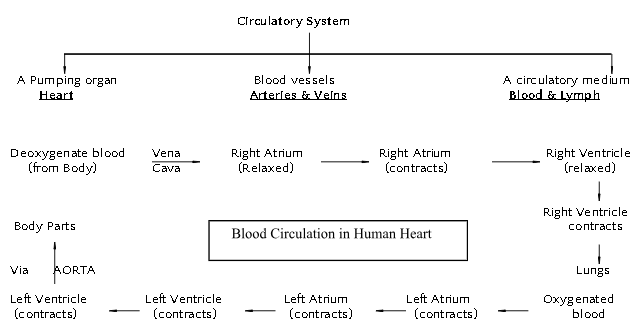
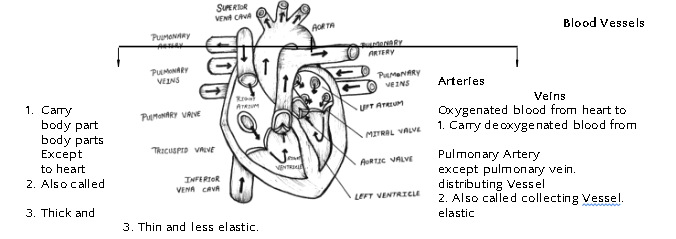
Human Heart
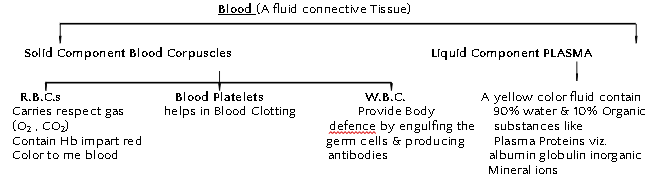
Lymph – a yellowish fluids escapes from the blood capillaries into the intercellular spaces contain less proteins than blood. Lymph flows from the tissues to the heart assisting in transportation and destroying germs.
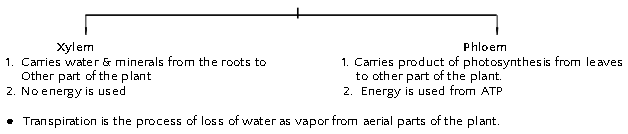
Transportation in Plants
There are two main conducting Pathways in a plant
EXCRETION
- The process of the removal of the harmful metabolic wastes from the body
- Excretory system of human beings includes :
- A pair of kidneys
- A Urinary Bladder
- A pair of ureter
- A Urethra
- Urine produced in the kidneys passes through the ureters into the urinary bladder where it is stored until it is released through the urethera.
- The purpose of making urine is to filter out waste product from the blood ie, urea which is produced in the liver.
- Each kidney has large numbers of filtration units called nephrons.
- The Urine formation involves three steps
- Glomerular Filtration: Nitrogenous wastes, glucose water, amino acid filter from the blood into Bowman Capsule of the nephron.
- Tubular reabsorption: Now, useful substances from the filtrate are reabsorbed back by capillaries surrounding the nephron.
3. Secretion: Extra, water, salts are secreted into the tubule which open up into the collecting duct & then into the ureter.
Hemodialysis: The process of purifying blood by an artificial kidney, it is meant for Kidney failure patient.
Excretion in Plants

- Other wastes may be stored in leaves, bark etc. which fall off from the plant.
- Plants excrete some waste into the soil around them.
- Gums, Resin In old Xylem
- Some metabolic wastes in the form of crystals of Calcium oxalates in the leaves of colocasia and stem of Zamikand